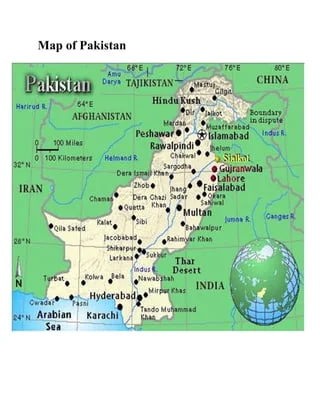
Pakistan’s geography plays a crucial role in shaping its development and environmental landscape. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the vast deserts of Baluchistan and the coastal regions along the Arabian Sea, the country’s diverse topography significantly influences its economic growth, natural resource management, and environmental sustainability.
Topographical Influence on Economic Development
The geographical features of Pakistan create distinct economic opportunities and challenges. The northern regions, dominated by the majestic Himalayas and the Karakoram Range, are rich in mineral resources and attract tourism, particularly in mountaineering and adventure sports. This sector not only generates income but also promotes infrastructure development in these remote areas.
Conversely, the fertile plains of Punjab and Sindh, watered by the Indus River system, are the backbone of Pakistan’s agriculture. This region accounts for a significant portion of the country’s food production, making it vital for both economic stability and food security. However, the reliance on irrigation from the Indus River also highlights challenges such as water scarcity and the need for sustainable water management practices.
Urban Development and Geographic Disparities
Urban areas like Karachi and Lahore, located in the coastal and central regions, serve as economic hubs. Karachi, as Pakistan’s largest city and a major port, facilitates international trade and commerce. The urban geography, however, leads to disparities in development. While cities experience growth and investment, rural areas often face neglect, leading to migration and increased pressure on urban infrastructure.
Environmental Challenges Linked to Geography
Pakistan’s diverse geography is not without its environmental challenges. The country is prone to natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, and landslides, primarily influenced by its topographical features. The monsoon season can lead to severe flooding, particularly in low-lying areas, devastating communities and agricultural lands. This necessitates robust disaster management strategies and resilient infrastructure to mitigate the impact of such events.
The arid regions, like the Thar Desert, face issues related to water scarcity and soil degradation. Climate change further exacerbates these problems, leading to unpredictable weather patterns and increased frequency of droughts. Addressing these challenges is critical for ensuring the sustainable development of these areas.
Biodiversity and Environmental Conservation
Pakistan’s varied geography also supports rich biodiversity. The northern mountains are home to unique wildlife, while coastal regions boast diverse marine ecosystems. However, environmental degradation, deforestation, and pollution threaten these natural habitats. The government and various NGOs are working to implement conservation efforts to protect endangered species and promote sustainable practices.
The establishment of national parks and wildlife reserves reflects an increasing recognition of the importance of environmental conservation. These efforts aim to balance development needs with ecological preservation, ensuring that natural resources are available for future generations.
Conclusion
The impact of geography on Pakistan’s development and environment is profound. While its diverse landscapes offer economic opportunities and rich biodiversity, they also present significant challenges that require thoughtful management and sustainable practices. Addressing the geographic disparities in development and implementing effective environmental policies will be essential for Pakistan’s future growth. By leveraging its geographical advantages while prioritizing sustainability, Pakistan can navigate the complex interplay between development and environmental stewardship, ensuring a resilient future for its people and the planet.
40 mini